Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of the service industry, businesses face increasing demands for personalization, responsiveness, and efficiency. Whether in hospitality, healthcare, finance, telecommunications, or professional services, customers today expect more than just the delivery of a service—they seek meaningful experiences. To meet these expectations, many service-based companies have turned to Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems as a strategic asset.
This article explores CRM in services, examining its role in improving customer engagement, streamlining operations, and enabling data-driven decision-making. It will also analyze CRM trends in various service sectors and offer practical insights into how companies can implement CRM effectively to drive growth and loyalty.
What Is CRM in Services?
CRM in services refers to the strategic use of technology and business processes to manage relationships with clients or customers in service-based industries. Unlike product-based businesses that focus on goods, service companies deliver intangible value, making customer interactions and relationships central to their success.
Key functions of CRM in service businesses include:
-
Tracking customer inquiries and requests
-
Managing appointments and service delivery
-
Automating marketing and communication
-
Collecting and analyzing customer data
-
Supporting after-service care and satisfaction surveys
By centralizing customer information and enabling better communication across departments, CRM systems help service providers deliver more personalized, consistent, and responsive experiences.
Why CRM Is Crucial for Service-Based Industries
1. Customer-Centric Operations
In service industries, the customer experience is the product. CRM platforms help service providers understand preferences, behavior, and pain points, allowing for more tailored services and proactive support.
2. Relationship Building
Service businesses often rely on long-term customer relationships. CRM tools maintain a history of interactions, enabling staff to engage clients in a more informed and empathetic manner.
3. Data-Driven Insights
With integrated analytics, CRM systems offer valuable insights into customer trends, staff performance, and service quality. These insights guide strategic decision-making and service improvements.
4. Increased Efficiency
CRM platforms automate repetitive tasks like appointment reminders, feedback collection, or follow-up emails. This improves internal efficiency and reduces operational costs.
5. Retention and Loyalty
CRM systems help identify at-risk customers and re-engage them through personalized campaigns. Better engagement leads to higher retention and stronger brand loyalty.
Core CRM Features for Service Businesses
-
Contact Management
Stores detailed customer profiles, including service history, preferences, notes, and communication logs. -
Service Scheduling
Enables efficient management of appointments, technicians, consultants, or staff availability. -
Automated Communications
Sends reminders, follow-ups, and satisfaction surveys automatically to maintain touchpoints. -
Customer Support Tools
Integrates help desks, ticketing, live chat, or chatbot functionalities for responsive issue resolution. -
Feedback and Satisfaction Tracking
Gathers post-service feedback and Net Promoter Scores (NPS) to evaluate service quality. -
Mobile Access
Provides mobile apps for field service agents or consultants to access customer data on the go. -
Analytics and Reporting
Offers dashboards to monitor KPIs such as customer satisfaction, service speed, and churn rates.
CRM Applications in Different Service Sectors
1. Healthcare
CRM in healthcare is used to manage patient engagement, from appointment scheduling to follow-up care. Features include:
-
Patient portals
-
Automated appointment reminders
-
Treatment history tracking
-
Feedback collection
-
HIPAA-compliant data security
Hospitals and clinics use CRM to reduce no-show rates, improve patient satisfaction, and build lasting relationships.
2. Hospitality and Tourism
Hotels, resorts, and travel agencies use CRM to personalize guest experiences, manage bookings, and build loyalty.
-
Guest profile management
-
Pre- and post-stay communication
-
Loyalty program integration
-
Feedback and review monitoring
CRM helps tailor experiences like room preferences, dining habits, and concierge services.
3. Financial Services
Banks, insurance companies, and fintech firms use CRM for:
-
Lead management and nurturing
-
Personalized product recommendations
-
Compliance tracking
-
Secure document management
These tools boost client trust and simplify complex financial service delivery.
4. Telecommunications
Telecom companies use CRM to handle:
-
Customer onboarding
-
Technical support ticketing
-
Plan upgrade notifications
-
Usage and billing information
CRM helps retain customers in an industry known for high churn.
5. Education and Training
Educational institutions use CRM for:
-
Student recruitment and admissions
-
Course registration and reminders
-
Alumni engagement
-
Donor management
This ensures smooth communication with prospective and current students, as well as alumni.
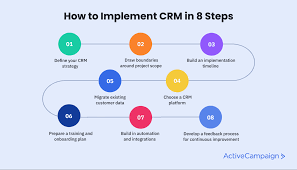
CRM Implementation Strategy for Service-Based Companies
1. Define Clear Goals
Begin with specific objectives such as improving response times, increasing client retention, or reducing service costs.
2. Map the Customer Journey
Understand how customers interact with your brand—from inquiry to service delivery and follow-up. This helps configure the CRM accordingly.
3. Choose the Right CRM Platform
Select a CRM that fits your business size, budget, and needs. Popular platforms include:
-
Salesforce Service Cloud
-
HubSpot Service Hub
-
Zoho CRM
-
Freshdesk
-
Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Customer Service
4. Train Staff Effectively
Ensure your team understands how to use the CRM tools. This includes training on data entry, ticket handling, and communication best practices.
5. Integrate with Existing Systems
Your CRM should connect with other tools such as:
-
Email marketing software
-
Billing or invoicing platforms
-
Booking systems
-
Customer support software
6. Monitor and Improve
Use CRM analytics to evaluate performance and continuously optimize your service delivery processes.
CRM Trends in the Service Industry
1. AI and Automation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming CRM systems through:
-
Predictive customer behavior modeling
-
AI-powered chatbots for 24/7 support
-
Automated case routing based on priority or issue type
2. Omnichannel Engagement
Modern CRMs unify communication across email, phone, social media, and SMS into a single dashboard, ensuring consistent service experiences.
3. Cloud-Based CRMs
Cloud CRMs allow remote access, real-time updates, and lower upfront costs. They are scalable and ideal for growing service businesses.
4. Personalization at Scale
Using data from CRM, businesses can deliver hyper-personalized services such as customized offers or individual service recommendations.
5. Customer Self-Service Portals
CRMs are now offering customer portals for:
-
Booking services
-
Checking service status
-
Downloading documents or invoices
-
Submitting feedback or complaints
This reduces support volume and empowers customers.
Benefits of CRM in Services
✔ Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Customers feel valued and understood, leading to higher satisfaction scores.
✔ Increased Revenue
Personalized up-selling and cross-selling boost revenue per customer.
✔ Better Internal Collaboration
Service teams access shared customer data, promoting teamwork and avoiding duplicated efforts.
✔ Faster Response Times
Automated workflows ensure that customer inquiries or complaints are addressed promptly.
✔ Greater Customer Retention
Timely follow-ups and loyalty programs keep customers engaged over the long term.
Challenges in CRM Adoption for Service Providers
-
Resistance to Change
Employees may be hesitant to adopt new systems without proper training or incentives. -
Data Silos
Poor integration with legacy systems can lead to fragmented customer data. -
Inadequate Customization
Off-the-shelf CRM solutions may not meet niche service requirements. -
Privacy Concerns
Managing sensitive customer information comes with legal and ethical responsibilities. -
Budget Constraints
Smaller service firms may struggle with high costs of premium CRM platforms.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Spa and Wellness Center
A wellness spa adopted Zoho CRM to manage bookings and customer profiles. Personalized service reminders and feedback collection improved client retention by 25% in one year.
Case Study 2: Legal Services Firm
A small law firm implemented Salesforce Service Cloud to track case communications and automate follow-ups. This reduced missed appointments and improved client satisfaction by 30%.
Case Study 3: Online Tutoring Platform
An e-learning provider used HubSpot to manage leads and student engagement. CRM insights helped tailor content to student needs, boosting course completion rates by 40%.
Future of CRM in Service Industries
The future of CRM in services will be shaped by:
-
Real-time analytics for instant decision-making
-
Voice-activated CRM for hands-free service management
-
Increased integration with IoT devices, e.g., connected appliances reporting service needs
-
Greater emphasis on customer privacy and ethical data use
-
Expanded use in niche sectors such as pet services, home repair, and freelance platforms
As customer expectations rise, CRM will be central to maintaining a competitive edge.
Conclusion
CRM in services is more than just a tool—it is a strategic philosophy centered around customer satisfaction, loyalty, and operational excellence. By integrating CRM into their daily operations, service providers can better understand their clients, deliver exceptional experiences, and grow sustainably in a highly competitive market.
From healthcare to hospitality and education to legal services, CRM empowers businesses to be more responsive, data-driven, and customer-focused. Despite challenges in adoption, the long-term rewards—enhanced trust, efficiency, and profitability—are well worth the investment.
For any service-based business aspiring to scale while keeping customer satisfaction at its core, CRM is not an option; it’s a necessity.