Introduction
In today’s fast-paced business environment, inventory management is more than just keeping track of stock—it’s about leveraging technology, data, and strategy to maintain a competitive edge. A robust business inventory program plays a pivotal role in ensuring that businesses can monitor, manage, and optimize their inventory effectively. From reducing holding costs to improving customer satisfaction, a well-implemented inventory program can be a game-changer for businesses of all sizes.
This comprehensive article will explore the concept of a business inventory program, its components, benefits, types, implementation strategies, challenges, and best practices to help enterprises navigate the complex landscape of inventory control.
1. What Is a Business Inventory Program?
A business inventory program is a software solution or system designed to help organizations manage the flow of goods, monitor stock levels, track orders, organize warehouse operations, and forecast future inventory needs. It automates and streamlines the entire inventory lifecycle, from procurement and storage to sales and delivery.
Key Objectives:
-
Maintain optimal stock levels
-
Prevent stockouts and overstocking
-
Reduce waste and shrinkage
-
Improve order accuracy and fulfillment speed
-
Provide real-time data and insights
2. The Importance of Inventory Management
Inventory is often one of the largest investments a business makes. Poor inventory management can lead to lost sales, customer dissatisfaction, cash flow issues, and storage problems. On the other hand, effective inventory management ensures:
-
Efficient use of capital
-
Seamless operations
-
Strong supplier relationships
-
Improved customer experiences
Especially in industries like retail, manufacturing, logistics, and e-commerce, inventory plays a crucial role in day-to-day operations.
3. Core Components of a Business Inventory Program
A modern inventory program typically consists of the following components:
A. Inventory Tracking
Tracks the movement and quantity of stock items in real-time across different locations.
B. Barcode and RFID Scanning
Facilitates fast and accurate tracking using barcode labels or RFID tags.
C. Order Management
Integrates purchasing and sales orders, ensuring accurate order processing.
D. Reporting and Analytics
Generates customizable reports on inventory turnover, reorder levels, and product performance.
E. Supplier and Vendor Management
Helps manage relationships and transactions with suppliers.
F. Demand Forecasting
Uses historical data and algorithms to predict future inventory needs.
G. Warehouse Management
Organizes stock locations, bin numbers, and warehouse workflows.
4. Types of Business Inventory Programs
Depending on the scale and nature of a business, there are various types of inventory programs:
A. Spreadsheets and Manual Systems
Used by small businesses; low-cost but prone to human error and inefficiency.
B. On-Premise Inventory Software
Installed locally on a company’s server, offering robust features but with higher upfront costs.
C. Cloud-Based Inventory Software
Accessible from anywhere, offers scalability, lower upfront costs, and automatic updates.
D. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
Integrated with other business functions (finance, HR, CRM); suitable for large enterprises.
E. Open-Source Inventory Software
Customizable and budget-friendly for companies with tech resources.
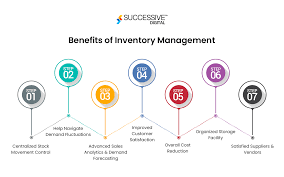
5. Benefits of Using a Business Inventory Program
Implementing an inventory program can transform the way a business operates:
A. Real-Time Visibility
Business owners and managers gain real-time insights into inventory status, reducing uncertainty.
B. Cost Reduction
Minimizes excess inventory, lowers holding costs, and avoids emergency restocking.
C. Better Customer Service
Ensures faster fulfillment, fewer backorders, and accurate delivery timelines.
D. Streamlined Operations
Automates repetitive tasks like reordering and inventory counts, improving productivity.
E. Data-Driven Decisions
Leverages analytics to identify trends, fast-moving products, and seasonal demand shifts.
F. Multi-Location Management
Ideal for businesses operating across various warehouses or retail outlets.
6. Choosing the Right Inventory Program
When selecting the ideal inventory solution, consider the following factors:
A. Business Size and Complexity
Startups may need basic tracking, while large retailers require advanced features.
B. Integration Needs
Ensure compatibility with existing tools like POS systems, accounting software, or ERP platforms.
C. Scalability
Choose a solution that can grow as your business expands.
D. User Interface
A simple and intuitive interface reduces the learning curve for staff.
E. Budget
Evaluate both upfront and recurring costs (licenses, support, updates).
F. Customization
Some businesses need industry-specific features, like lot tracking or expiration management.
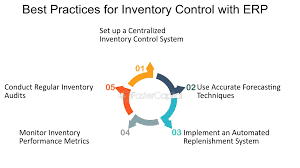
7. Steps to Implement a Business Inventory Program
Proper implementation is key to realizing the full benefits of an inventory system:
Step 1: Assess Current Inventory Process
Document existing workflows, challenges, and objectives.
Step 2: Select the Right Software
Compare features, pricing, and user reviews. Request demos or trials.
Step 3: Clean Up Inventory Data
Before migration, remove outdated, duplicate, or incorrect records.
Step 4: Train Employees
Provide adequate training on how to use the new system effectively.
Step 5: Integrate with Existing Systems
Ensure seamless data exchange between inventory, sales, accounting, and e-commerce platforms.
Step 6: Test the System
Run a pilot program to catch potential bugs or user issues.
Step 7: Go Live and Monitor Performance
Monitor KPIs like stock turnover ratio, order accuracy, and fulfillment speed.
8. Challenges in Inventory Management
Despite having an advanced system, businesses may face inventory challenges such as:
A. Inaccurate Forecasting
Misjudging demand can lead to overstock or stockouts.
B. Inventory Shrinkage
Losses due to theft, damage, or misplacement.
C. Lack of Standardization
Disorganized processes across departments or locations.
D. Supplier Delays
Interruptions in the supply chain can disrupt inventory levels.
E. User Resistance
Employees may resist change due to fear of complexity or job impact.
Solutions:
-
Use predictive analytics
-
Conduct regular audits
-
Set clear SOPs
-
Maintain strong supplier communication
-
Offer change management training
9. Industry Use Cases
Retail Industry
Manages thousands of SKUs across multiple stores and warehouses. Needs real-time stock updates, auto-reordering, and seamless POS integration.
E-Commerce Businesses
Require integration with online platforms like Shopify or WooCommerce, and features like dropshipping and shipping label generation.
Manufacturing Companies
Need raw material tracking, bill of materials (BOM) management, and work-in-progress (WIP) monitoring.
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
Focus on lot tracking, expiration dates, and compliance with regulations (FDA, HIPAA).
Food and Beverage
Must manage perishable inventory, FIFO (First-In, First-Out) systems, and seasonal demand.
10. Best Business Inventory Programs in 2025
Here are some leading inventory software solutions:
1. NetSuite ERP
Comprehensive ERP with strong inventory, finance, and CRM integration.
2. TradeGecko (Now QuickBooks Commerce)
User-friendly interface with solid e-commerce integrations.
3. Zoho Inventory
Affordable cloud-based platform for small to mid-sized businesses.
4. Fishbowl Inventory
Popular among manufacturers and warehouses, integrates with QuickBooks.
5. Cin7
Good for retail and B2B, with built-in POS and warehouse tools.
6. inFlow Inventory
Simple solution for small businesses; supports barcoding and invoicing.
11. Future Trends in Inventory Management
As technology evolves, so does inventory control. Expect to see:
A. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI-driven forecasting, demand sensing, and inventory optimization.
B. Internet of Things (IoT)
Smart sensors in warehouses to track real-time stock movement.
C. Blockchain
Enhanced traceability and transparency across the supply chain.
D. Mobile Apps
Mobile-first platforms for inventory tracking on the go.
E. Drones and Robotics
Automation of warehouse operations and real-time scanning.
12. Conclusion
A business inventory program is more than a digital ledger—it’s a strategic asset that drives operational excellence, customer satisfaction, and profitability. Whether you’re a small e-commerce brand or a multinational manufacturer, the right inventory system can streamline your processes, reduce costs, and position your business for growth.
Investing in a modern inventory solution is not just a technological upgrade; it’s a business necessity. With thoughtful planning, the right tools, and a commitment to continuous improvement, your organization can master inventory management and unlock long-term success.